OBESITY AND BARIATRIC SURGERY
You might have seen fig fat peoples around you once in a life time. Frequently we see these obese individuals in movies or documentries. When we se them we get only one question in our mind that why therse peoples the way they are. For most of the viewers it becomes a matter of laughing after seeing these individuals. But its a matter of concern as obesity has been classified as a disease. obesity could be due to many reasons. for some it may be due to some emnzyme deficiency while for most it is familial or hereditary. some have its relation with mutation in the ob gene which gives rise to the familial type of obesity. It is necessary to take treatment, medical or surgical as soon as possible as it is related to many ill health effects.
Obesity means having too much body fat. It is different from being overweight, which means weighing too much. The weight may come from muscle, bone, fat and/or body water. Both terms mean that a person's weight is greater than what's considered healthy for his or her height.
Obesity occurs over time when you eat more calories than you use. The balance between calories-in and calories-out differs for each person. Factors that might tip the balance include your genetic makeup, overeating, eating high-fat foods and not being physically active.
Being obese increases your risk of diabetes, heart disease, stroke, arthritis and some cancers. If you are obese, losing even 5 to 10 percent of your weight can delay or prevent some of these diseases. Here we will discuss about the Surgical management for obesity which is known as bariatric surgery.
Bariatric surgery (weight-loss surgery) includes a variety of procedures performed on people who are obese. Weight loss is achieved by reducing the size of the stomach with a gastric band or through removal of a portion of the stomach or by resecting and re-routing the small intestines to a small stomach pouch (gastric bypass surgery).The U.S. National Institutes of Health recommends bariatric surgery for obese people with a body mass index (BMI) of at least 40, and for people with BMI 35 and serious coexisting medical conditions such as diabetes.
Classification of
surgical procedures
Predominantly
malabsorptive procedures
Predominantly malabsorptive
procedures, although they also reduce stomach size, these operations are based
mainly on creating malabsorption.
 This complex
operation is termed biliopancreatic diversion (BPD) or the Scopinaro
procedure. The original form of this procedure is now rarely performed
because of problems with malnourishment. It has been replaced with a modification
known as duodenal switch (BPD/DS). Part of the stomach is resected, creating a
smaller stomach (however the patient can eat a free diet as there is no
restrictive component). The distal part of the small intestine is then
connected to the pouch, bypassing the duodenum and jejunum.
This complex
operation is termed biliopancreatic diversion (BPD) or the Scopinaro
procedure. The original form of this procedure is now rarely performed
because of problems with malnourishment. It has been replaced with a modification
known as duodenal switch (BPD/DS). Part of the stomach is resected, creating a
smaller stomach (however the patient can eat a free diet as there is no
restrictive component). The distal part of the small intestine is then
connected to the pouch, bypassing the duodenum and jejunum.
In around 2% of
patients there is severe malabsorption and nutritional deficiency that
requires restoration of the normal absorption. The malabsorptive effect of BPD
is so potent that those who undergo the procedure must take vitamin and dietary
minerals above and beyond that of the normal population. Without these
supplements, there is risk of serious deficiency diseases such as anemia and osteoporosis.
Jejunoileal
bypass
This procedure
is no longer performed.
Procedures that
are solely restrictive, act to reduce oral intake by limiting gastric volume,
produces early satiety, and leave the alimentary canal in continuity,
minimizing the risks of metabolic complications.
Vertical banded
gastroplasty
In the vertical
banded gastroplasty, also called the Mason procedure or stomach stapling, a
part of the stomach is permanently stapled to create a smaller pre-stomach
pouch, which serves as the new stomach.
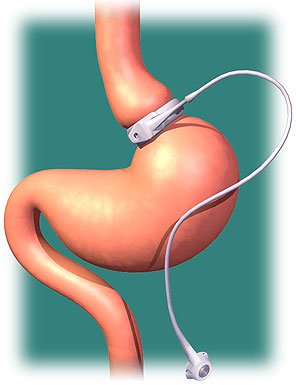
The restriction
of the stomach also can be created using a silicone band, which can be adjusted
by addition or removal of saline through a port placed just under the skin.
This operation can be performed laparoscopically, and is commonly referred to
as a "lap band".
Weight loss is predominantly due to the restriction of nutrient intake that is
created by the small gastric pouch and the narrow outlet.
Sleeve
gastrectomy
Sleeve
gastrectomy, or gastric sleeve, is a surgical weight-loss procedure in which
the stomach is reduced to about 15% of its original size, by surgical removal
of a large portion of the stomach, following the major curve. The open edges
are then attached together (typically with surgical staples, sutures, or both)
to leave the stomach shaped more like a tube, or a sleeve, with a banana shape.
The procedure permanently reduces the size of the stomach. The procedure is
performed laparoscopically and is not reversible.
Stomach volume is reduced, but it
tends to function normally so most food items can be consumed in small
amounts.
Removes the portion of the stomach
that produces the hormones that stimulates hunger (Ghrelin), although the
durability of this removal has yet to be confirmed.
Dumping syndrome is less likely
due to the preservation of the pylorus (although dumping can occur anytime
stomach surgery takes place).
Minimizes the chance of an ulcer
occurring.
By avoiding the intestinal bypass,
the chance of intestinal obstruction (blockage), anemia, osteoporosis,
protein deficiency and vitamin deficiency are significantly reduced.
Very effective as a first stage
procedure for high BMI patients (BMI >55 kg/m2).
Limited results appear promising
as a single stage procedure for low BMI patients (BMI 35–45 kg/m2).
Appealing option for people with
existing anemia, Crohn's disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and numerous
other conditions that make them too high risk for intestinal bypass
procedures.
Intragastric
balloon (gastric balloon)
Intragastric
balloon involves placing a deflated balloon into the stomach, and then filling
it to decrease the amount of gastric space. The balloon can be left in the
stomach for a maximum of 6 months. The intragastric balloon may be used prior
to another bariatric surgery in order to assist the patient to reach a weight
which is suitable for surgery, further it can also be used on several occasions
if necessary.
Gastric
Plication
Basically, the
procedure can best be understood as a version of the more popular gastric
sleeve or gastrectomy surgery where a sleeve is created by suturing rather than
removing stomach tissue thus preserving its natural nutrient absorption
capabilities. Gastric Plication significantly reduces the volume of the
patient's stomach, so smaller amounts of food provide a feeling of satiety. The
study describes gastric sleeve plication (also referred to as gastric imbrication or laparoscopic
greater curvature plication) as a restrictive technique that
eliminates the complications associated with adjustable gastric
banding and vertical sleeve gastrectomy—it does this by creating
restriction without the use of implants and without gastric resection (cutting)
and staples.
A common form
of gastric bypass surgery is the Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Here, a small
stomach pouch is created with a stapler device, and connected to the distal
small intestine. The upper part of the small intestine is then reattached in a
Y-shaped configuration.A factor in the
success of any bariatric surgery is strict post-surgical adherence to a
healthier pattern of eating.
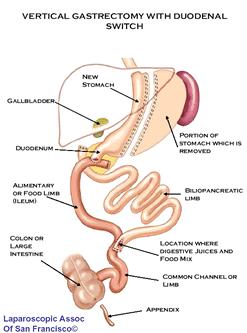
Sleeve
gastrectomy with duodenal switch
A variation of
the biliopancreatic diversion includes a duodenal switch. The part of the stomach
along its greater curve is resected. The stomach is "tubulized" with
a residual volume of about 150 ml. This volume reduction provides the food
intake restriction component of this operation. This type of gastric resection
is anatomically and functionally irreversible. The stomach is then disconnected
from the duodenum and connected to the distal part of the small intestine. The
duodenum and the upper part of the small intestine are reattached to the rest
at about 75–100 cm from the colon.
Implantable
gastric stimulation
This procedure
where a device similar to a heart pacemaker is implanted by a surgeon, with the
electrical leads stimulating the external surface of the stomach, is being
studied in the USA. Electrical stimulation is thought to modify the activity of
the enteric nervous system of the stomach,
which is interpreted by the brain to give a sense of satiety, or fullness.
Early evidence suggests that it is less effective than other forms of bariatric
surgery.
Eating after
bariatric surgery
Post-surgery,
overeating is curbed because exceeding the capacity of the stomach causes nausea
and vomiting. Diet restrictions after recovery from surgery depend in part on
the type of surgery. Many patients will need to take a daily multivitamin pill for
life to compensate for reduced absorption of essential nutrients. Because
patients cannot eat a large quantity of food, physicians typically recommend a
diet that is relatively high in protein and low in fats and alcohol.
Fluid
recommendations
It is very
common, within the first month post-surgery, for a patient to undergo volume
depletion and dehydration. Patients have difficulty drinking the appropriate
amount of fluids as they adapt to their new gastric volume. Limitations on oral
fluid intake, reduced calorie intake, and a higher incidence of vomiting and
diarrhea are all factors that have a significant contribution to dehydration.
Effectiveness
of surgery
Weight loss
Biliopancreatic diversion — 117
Lbs / 53 kg
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) —
90 Lbs / 41 kg
Open — 95 Lbs/ 43 kg
Laparoscopic — 84 Lbs / 38 kg
Vertical banded gastroplasty — 71
Lbs / 32 kg
Laparoscopic
bariatric surgery requires a hospital stay of only one or two days. Short-term
complications from laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding are reported to be
lower than laparoscopic Roux-en-Y surgery, and complications from laparoscopic
Roux-en-Y surgery are lower than conventional (open) Roux-en-Y surgery.
Adverse effects
Complications
from weight loss surgery are frequent. Common problems were gastric dumping
syndrome in about 20% (bloating and diarrhea after eating, necessitating small
meals or medication), leaks at the surgical site (12%), incisional hernia (7%),
infections (6%) and pneumonia (4%). Mortality was 0.2%. As the rate of
complications appears to be reduced when the procedure is performed by an
experienced surgeon, guidelines recommend that surgery be performed in
dedicated or experienced units.
Metabolic bone
disease manifesting as osteopenia and secondary hyperparathyroidism have been
reported after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery due to reduced calcium
absorption. The highest concentration of calcium transporters is in the
duodenum. Since the ingested food will not pass through the duodenum after a
bypass procedure, calcium levels in the blood may decrease, causing secondary
hyperparathyroidism, increase in bone turnover, and a decrease in bone mass.
Increased risk of fracture has also been linked to bariatric surgery.
Rapid weight
loss after obesity surgery can contribute to the development of gallstones as
well by increasing the lithogenicity of bile Nutritional derangements due to
deficiencies of micronutrients like iron, vitamin B12, fat soluble vitamins,
thiamine, and folate are especially common after malabsorptive bariatric
procedures. Seizures due to hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia have been reported.
Inappropriate insulin secretion secondary to islet cell hyperplasia, called
pancreatic nesidioblastosis, might explain this syndrome.


Great post! My sister is thinking about getting bariatric surgery in Oklahoma City so I have been doing research trying to find the advantages and disadvantages. She has tried every diet and workout plan there is and nothing seems to work for her. Maybe this is the way to go. Thanks so much for sharing, I will have to send this to her.
ReplyDeleteThat is just awesome thing to share here. I am new to your blog but loving your writing skills and travel adventures. Some very vital things to bear in mind while traveling. thanks for sharing.
ReplyDeletegreat blog prashant !!! thx fr sharing n keep it up !!!! :)
ReplyDeleteLaparoscopic Roux en Y Gastric Bypass Surgery procedure, a portion of the stomach is stapled and thus reduced its size. Then the small intestaine is connected to the reduced portion of the stomach.
ReplyDeleteAshmita
This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteI hear ya! Chinese dishes are way too oily. I commented on your blog before about oily Chinese dishes. I am an expat Chinese. After many years in the U.S. and actually trying out different food other than Chinese, I can never go back to Chinese dishes again. Whenever I crave for Chinese food now, I would go with Thai and Korean food instead. We Chinese want to believe our food is the best cusine in the world, as a Chinese saying goes (eat in China). The fact is that Chinese people are among the world's highest percentage of stomach and liver cancer patients, both of which are food induced. Another problem with Chinese dishes is that it's generally too salty, which contributes to high blood pressure. Again, Chinese folks are inproportionally more likely to suffer from high blood pressure.
ReplyDeleteتركيب بالون المعده
بالون المعدة
بالونات المعدة
عملية البالون
عملية بالون المعدة
"Awesome read and it's nice to get some perspective from someone with experience"!!
ReplyDeleteBest doctor for Pacemaker surgery in Indore
Welcome to Escorts In Doha agency, we are the best-diagrammed agency for men of their word elite comicalness administrations to give industry top ranking Escorts in Doha.
ReplyDeleteNice article by the author.For more information visit Gastric Balloon
ReplyDeleteMy husband and i ended up being happy that Emmanuel managed to carry out his investigation because of the ideas he grabbed from your own blog. It’s not at all simplistic to simply choose to be giving away strategies which often men and women could have been selling. We really acknowledge we’ve got you to appreciate for this. The most important explanations you have made, the simple web site navigation, the friendships you will help instill – it’s got everything fantastic, and it is helping our son and us understand the subject matter is excellent, and that’s tremendously pressing. Thanks for the whole thing! Covid Test stoke on trent
ReplyDelete